On August 28, 2021, China Association for Conservation Technology of Cultural Heritage (CACTCH) called an achievements appraisal conference on “Key technology research an/d product development for immunodetection of textile cultural relics in archaeological sites” in Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province. This achievement was jointly developed by Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, China National Silk Museum an/d Dunhuang Academy.

The main component of textiles is natural macromolecular protein, which will deteriorate an/d degrade under the influence of a variety of factors in the underground confined environment. When unearthed, most textiles have been muddied, mineralized or even left only a few tiny traces, so it is difficult to distinguish the types of textile cultural relics. In the past ten years, the team adopted immunological methods an/d developed a set of rapid qualitative analysis methods suitable for archaeological sites through simple steps.
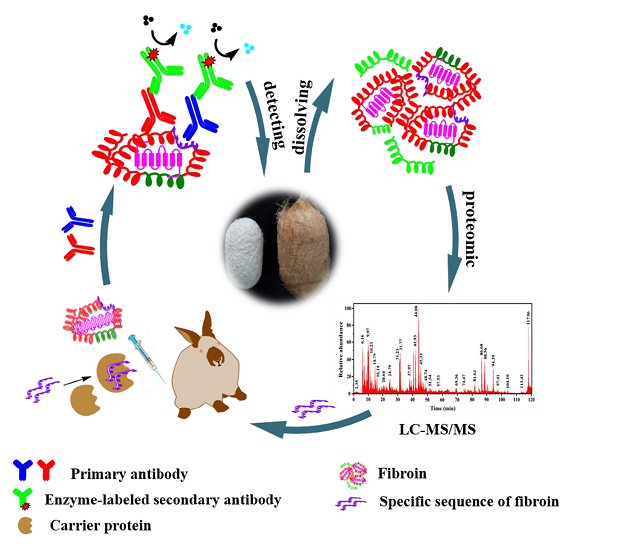

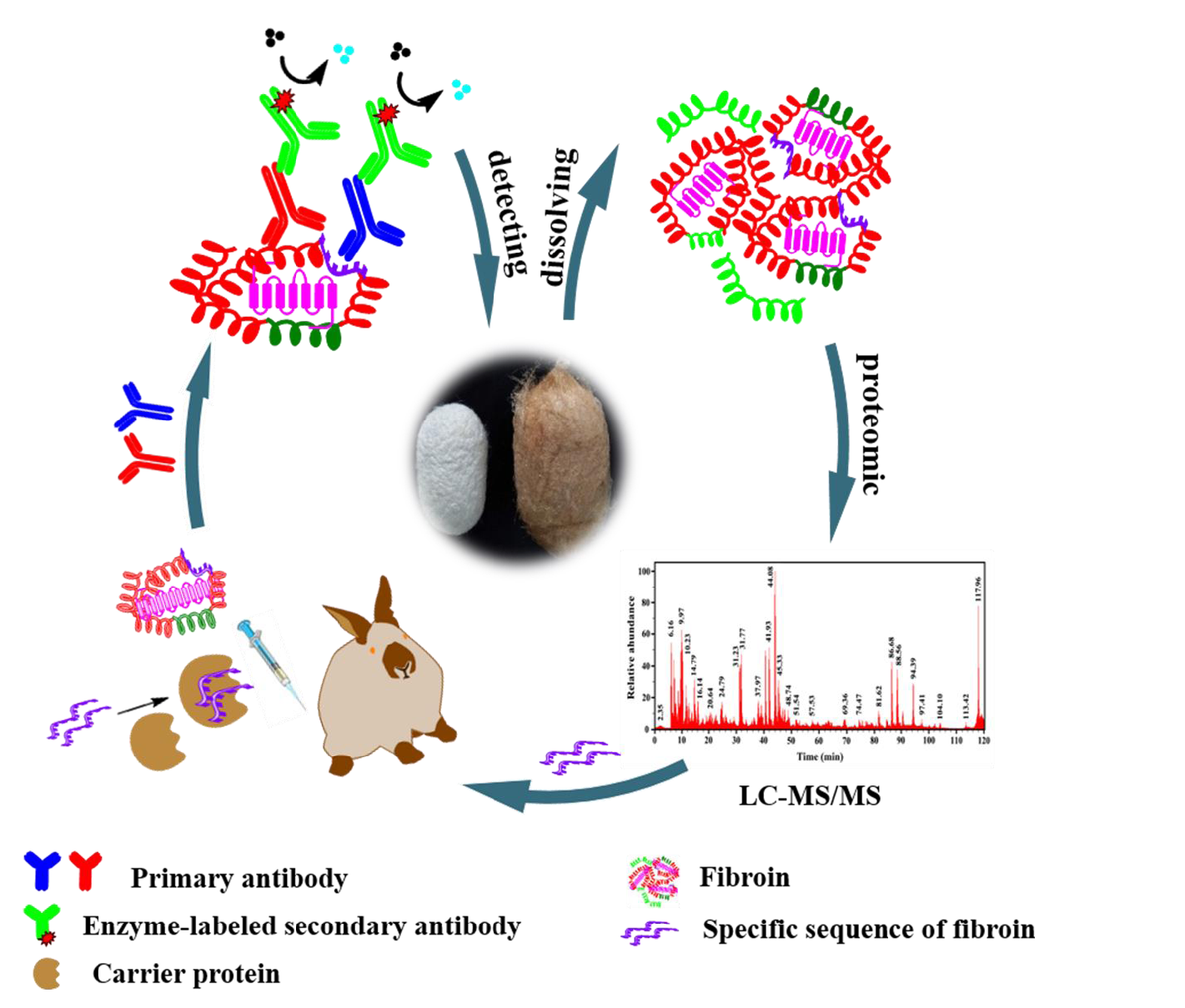
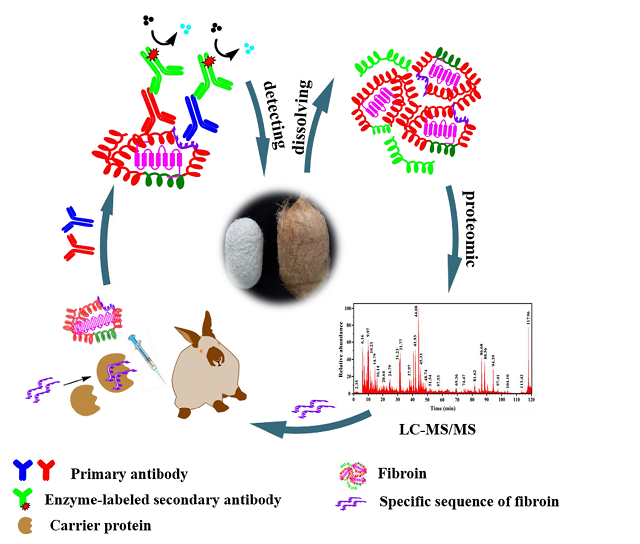

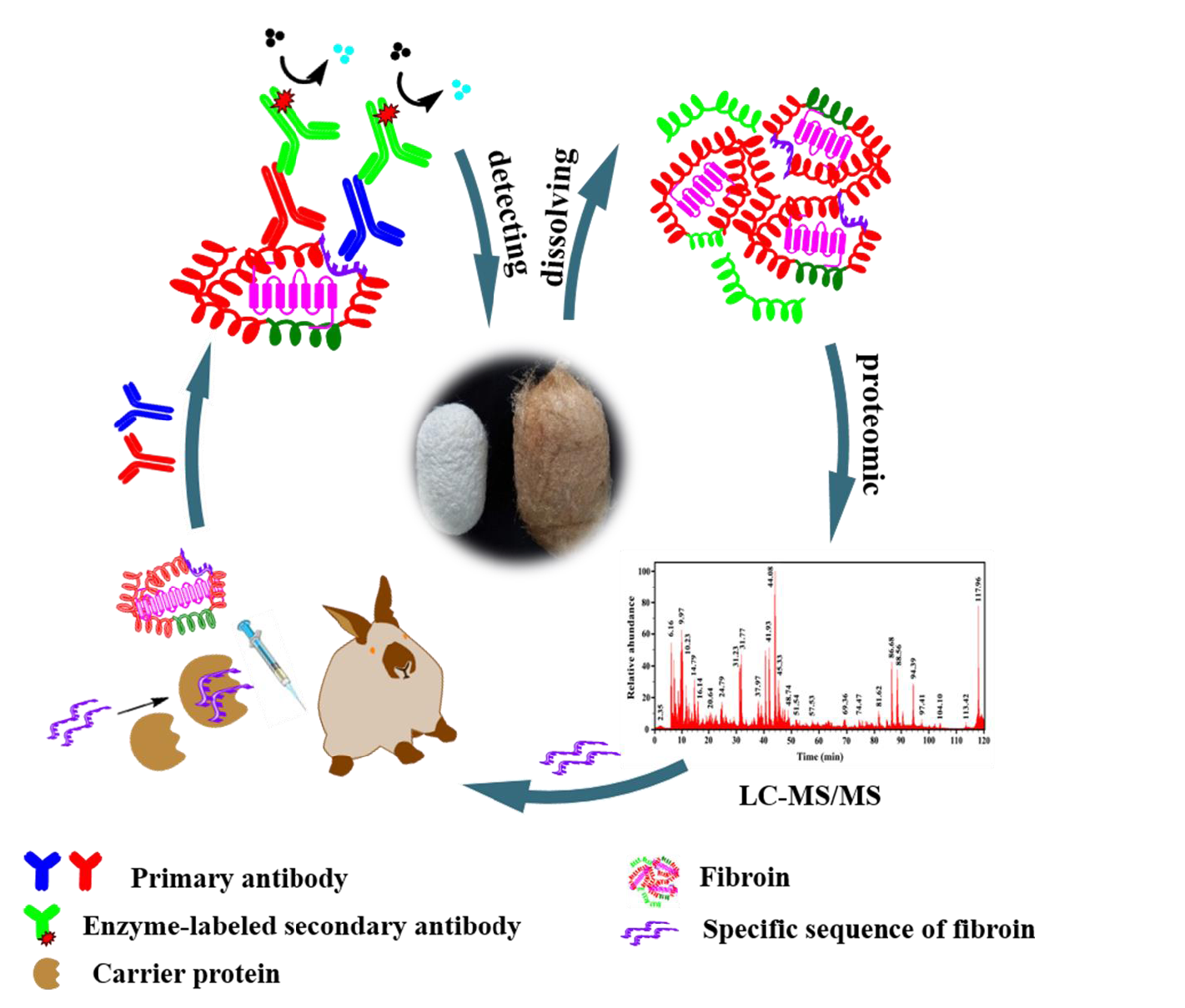
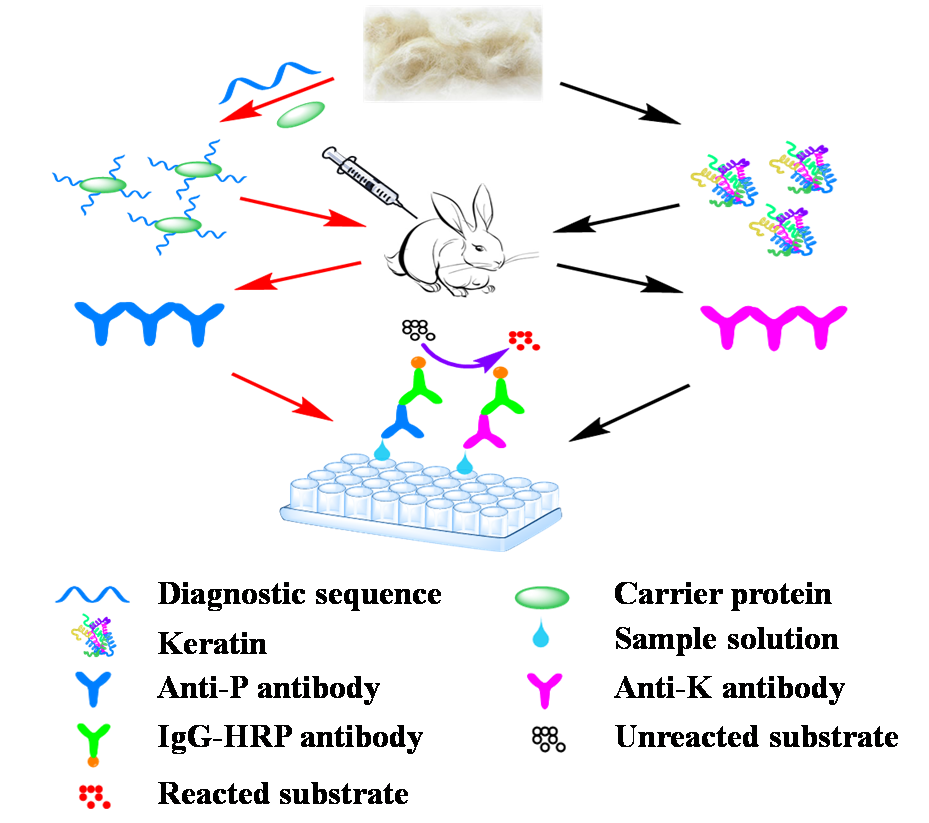
Through proteomic analysis, the team obtained the diagnostic sequences of silk fibroin an/d keratin of different biological species. Polyclonal antibody an/d monoclonal antibody of silk fibroin an/d keratin were prepared by animal immunization with high sensitivity an/d specificity. Through enzyme linked immunosorbent assay, immunofluorescence microscopy, Western blot, electrochemical immunosensor an/d other methods, the detection system of textile cultural relics was constructed an/d the limit of detection could reach 10-12 g/mL. Moreover, Colloidal gold immunochromatographic assay strip an/d time-resolved fluorescence immunochromatographic assay strip were developed an/d successfully applied in archaeological sites, which firstly provided a sensitive, specific an/d fast identification method for finding invisible ancient textile residues.

Silk fibroin assay kit available in market
Up to now, the team has published dozens of high-level papers in this field. Moreover, 37 national invention patents have been authorized an/d two monographs have been published. In particular, the antibody-based immunological method has been employed for the detection of ancient textile traces in more than 20 major archaeological sites.
The immunodetection technology of textile cultural relics has become an important identification method to reveal protein textile residues in ancient ruins. The method also provides a number of important archaeological evidence for the origin of silk an/d the cultural exchange along the Silk Road. Furthermore, the method offers important support to construct the Chinese characteristic archeology which has significant cultural benefits.
 Pay attention to us
×
Pay attention to us
×